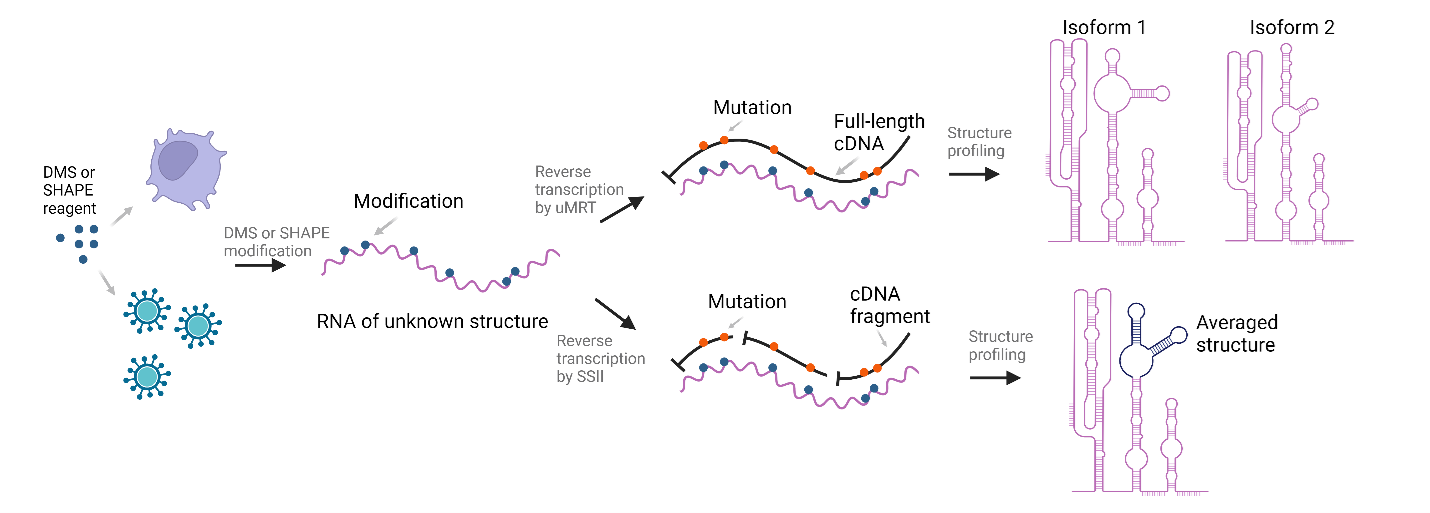
Structure profiling and natural modification detection with UltraMarathonRT
UltraMarathonRT is the ultimate solution for efficient, full-length cDNA synthesis from long RNA templates. It has been engineered to bind tightly to RNA templates, ensuring minimal dissociation and exceptional end-to-end processivity, making it ideal for RNA structure profiling. Combining the full-length cDNA synthesized by uMRT with nanopore long-read sequencing enables accurate, in-depth structural analysis that provides visibility into distinct structural isoforms which cannot be discerned using traditional, distributive RTs (ref: Nature Methods (2023) 20, 849–859 and Nature Protocols (2024) 19, 1835–1865).
UltraMarathonRT offers superior accuracy with lower background error rates compared to traditional reverse transcriptases. By minimizing false-positive mutations, uMRT provides reliable detection of chemical modifications and precise analysis of RNA structural features, ensuring more accurate results in your research.
UltraMarathonRT generates unique mutational signatures on DMS modified uracil (U) and guanine (G), making it the only RT enzyme that can accurately detect DMS-induced modifications on all four RNA bases—adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine (ref: Nucleic Acids Research (2023) 51, 8744–8757). This expands RNA structural profiling, offering comprehensive nucleotide-level insights, even for previously challenging bases like guanine.
UltraMarathonRT enables more sensitive and high-resolution single-molecule analysis. This is crucial for detecting correlated modification events, which are used to infer secondary and tertiary structures, as well as dynamic structural states in RNA molecules.
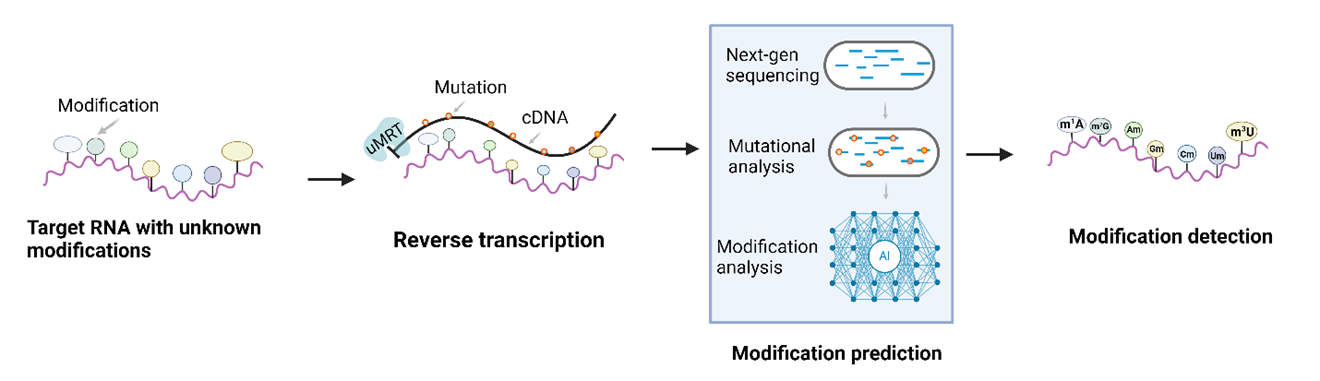
UltraMarathonRT is also sensitive to other RNA modifications, making it the first epitranscriptomic tool that detects post-transcriptional modifications (ref: Journal of Molecular Biology (2023), 435, 168299).